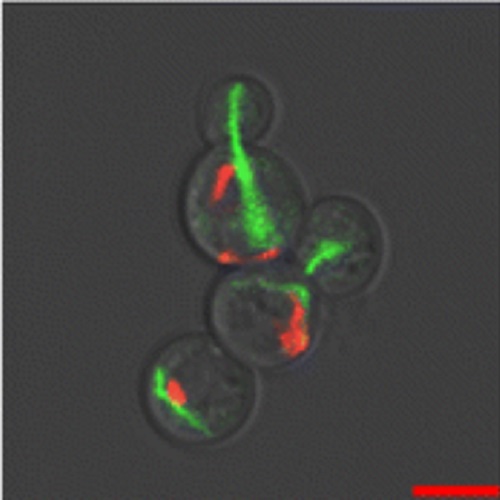
Expression and assembly of recombinant surface layer proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Most bacterial surface layers (SLs) are formed by self-assembly of a single type of protein. Native and recombinant surface layer monomers are capable to self-assemble on solid substrates and in solution to highly regular nanosized arrays which make them attractive for nanobiotechnological applications. In this study, we expressed the surface layer protein SbsC of Bacillus stearothermophilus ATTC 12980, tagged with Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein, in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We observed a network of tubular structures in the cytosol of the transformed yeast cells that did not colocalize with microtubules or the actin cytoskeleton. Time-resolved analysis of the formation of these structures during vegetative growth and sporulation was investigated by live fluorescence microscopy. While in meiosis ascospores seemed to receive assembled structures from the diploid cells, during mitosis, SL structures were formed de novo in the buds. SL assembly always started with the appearance of a dot-like structure in the cytoplasm, suggesting a single nucleation point.
Back to list