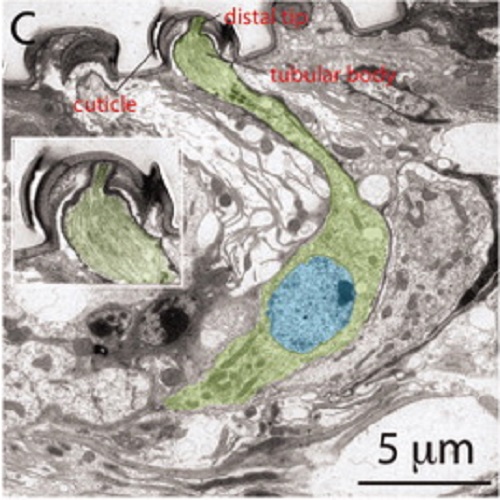
NOMPC, a member of the TRP channel family, localizes to the tubular body and distal cilium of Drosophila campaniform and chordotonal receptor cells.
Mechanoreception underlies the senses of touch, hearing and balance. An early event in mechanoreception is the opening of ion channels in response to mechanical force impinging on the cell. Here, we report antibody localization of NOMPC, a member of the transient receptor potential (TRP) ion channel family, to the tubular body of campaniform receptors in the halteres and to the distal regions of the cilia of chordotonal neurons in Johnston's organ, the sound-sensing organ of flies. Because NOMPC has been shown to be associated with the mechanotransduction process, our studies suggest that the transduction apparatus in both types of sensory cells is located in regions where a specialized microtubule-based cytoskeleton is in close proximity to an overlying cuticular structure. This localization suggests a transmission route of the mechanical stimulus to the cell. Furthermore, the commonality of NOMPC locations in the two structurally different receptor types suggests a conserved transduction apparatus involving both the intracellular cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix.
- Cytoskeleton (Hoboken) 2011 Jan;68(1):1-7
- 2011
- Cell Biology
- 21069788
- PubMed
Enabled by:
