Direct mechanical measurements reveal the material properties of three-dimensional DNA origami.
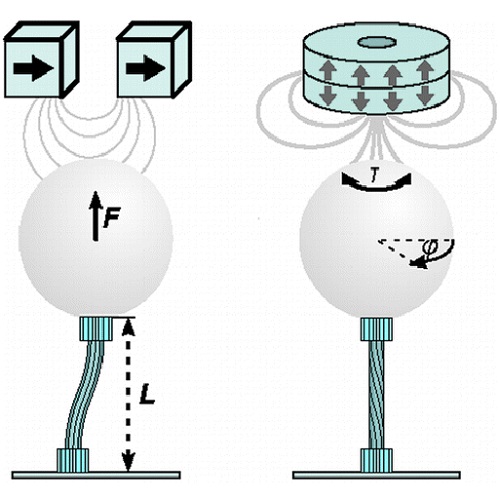
The application of three-dimensional DNA origami objects as rigid mechanical mediators or force sensing elements requires detailed knowledge about their complex mechanical properties. Using magnetic tweezers, we directly measure the bending and torsional rigidities of four- and six-helix bundles assembled by this technique. Compared to duplex DNA, we find the bending rigidities to be greatly increased while the torsional rigidities are only moderately augmented. We present a mechanical model explicitly including the crossovers between the individual helices in the origami structure that reproduces the experimentally observed behavior. Our results provide an important basis for the future application of 3D DNA origami in nanomechanics.
- Nano Lett. 2011 Dec 14;11(12):5558-63
- 2011
- Biophysics
- 22047401
- PubMed
Enabled by:
