Specific polar subpopulations of astral microtubules control spindle orientation and symmetric neural stem cell division.
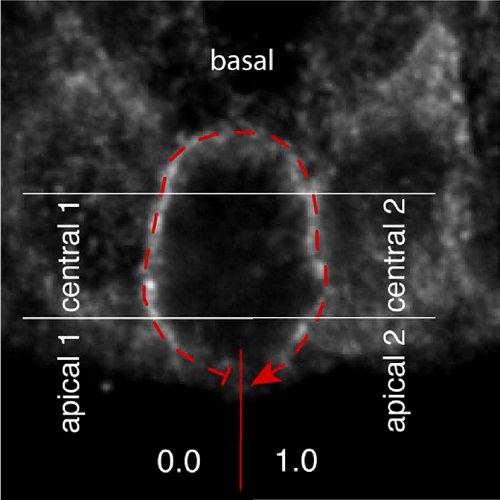
Mitotic spindle orientation is crucial for symmetric vs asymmetric cell division and depends on astral microtubules. Here, we show that distinct subpopulations of astral microtubules exist, which have differential functions in regulating spindle orientation and division symmetry. Specifically, in polarized stem cells of developing mouse neocortex, astral microtubules reaching the apical and basal cell cortex, but not those reaching the central cell cortex, are more abundant in symmetrically than asymmetrically dividing cells and reduce spindle orientation variability. This promotes symmetric divisions by maintaining an apico-basal cleavage plane. The greater abundance of apical/basal astrals depends on a higher concentration, at the basal cell cortex, of LGN, a known spindle-cell cortex linker. Furthermore, newly developed specific microtubule perturbations that selectively decrease apical/basal astrals recapitulate the symmetric-to-asymmetric division switch and suffice to increase neurogenesis in vivo. Thus, our study identifies a novel link between cell polarity, astral microtubules, and spindle orientation in morphogenesis.
- Elife 2014 Jul 04;3
- 2014
- Cell Biology
- 24996848
- PubMed
Enabled by:
