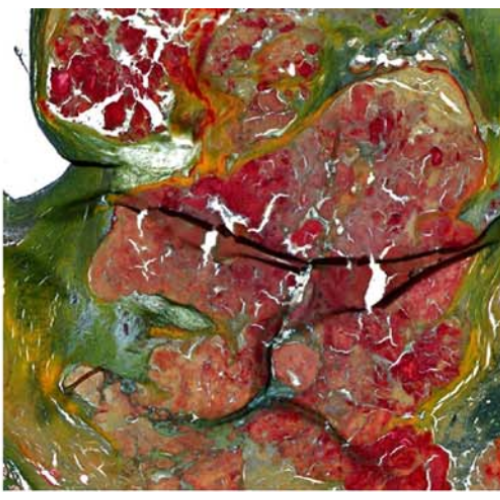
Movat Pentachrom stain reveals unexpected high osteogenesis rate in aortic valves.
BACKGROUND AND AIM OF THE STUDY: Aortic valve (AV) stenosis is the most common valvular heart disease with an incidence of 3% for people ≥ 65years in the industrialized world with indication for a surgical or transcatheter valve replacement. Researchers suppose osteogenic processes as key mechanisms in calcific aortic valve stenosis. Recently, Torre et al. published impressive histological analyses and detected osseous and/or chondromatous metaplasia in 15.6% of 6685 native calcified aortic valves. Therefore one HE section per valve originated from the area with the greatest extent of calcification was analyzed. Aim of our experimental setup was to identify regions of neo-osteogenesis and to determine the rate of specimens with active mineralization in human aortic valve tissue by Movat Pentachrom staining of sections of lager tissue segments. METHODS: Operational replaced aortic valves of 35 patients, 15 female and 20 male with an average age of 66.2 years were formalin fixed and decalcified using Osteosoft®-solution. Tissue samples were cut and 2μm specimens were stained with Movat Pentachrom to visualize osteogenic regions. Instead of screening a large number of sections, tissue samples were cut up to five times with at least 100μm space each if no region of osseous and/or chondromatous metaplasia was visible. RESULTS/CONCLUSIONS: Using this setup, a region of osseous metaplasia was detected in 25 (71.4%) of 35 samples analyzed. In some cases, these regions were small sized and only visible due to the bright color of Movat Pentachrom stain. This leads to the suggestion that a higher rate of calcified aortic valve samples would be classified as cusps with areas of neo-osteogenesis after staining with Movat Pentachrom stain and by the systematic analysis of larger parts of the tissue blocks.
- Acta Histochem. 2017 Jun;119(5):533-537
- 2017
- Medical Biology
- 28579288
- PubMed
Enabled by:
