The F-actin modulator SWAP-70 controls podosome patterning in osteoclasts.
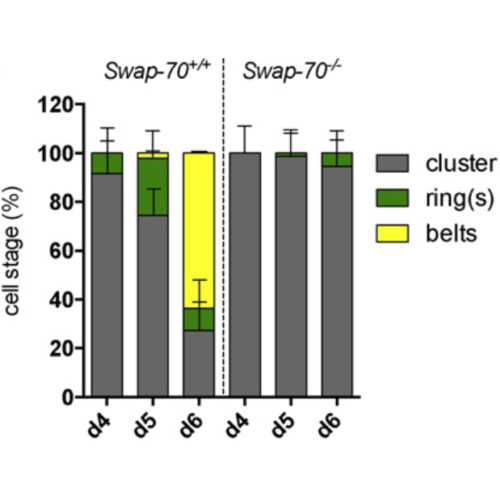
Osteoclasts are bone resorbing cells acting as key mediators of bone disorders. Upon adhesion to bone, osteoclasts polarize and reorganize their cytoskeleton to generate a ring-like F-actin-rich structure, the sealing zone, wherein the osteoclast's resorptive organelle, the ruffled border, is formed. The dynamic self-organization of actin-rich adhesive structures, the podosomes, from clusters to belts is crucial for osteoclast-mediated bone degradation. Mice lacking the protein SWAP-70 display an osteopetrotic phenotype due to defective bone resorption caused by impaired actin ring formation in Swap-70-/- osteoclasts. To further elucidate the mechanisms underlying this defect, we investigated the specific function of SWAP-70 in the organization and dynamics of podosomes. These detailed studies show that the transition from podosome clusters to rings is impaired in Swap-70-/- osteoclasts. Live cell imaging of dynamic F-actin turnover and SWAP-70 localization during podosome patterning indicate that SWAP-70 is dispensable for cluster formation but plays a key role in F-actin ring generation. Our data provide insights in the role of SWAP-70's F-actin binding domain and pleckstrin homology (PH) domain in the proper localization of SWAP-70 and formation of a peripheral podosome belt, respectively. Ex vivo bone analyses revealed that SWAP-70-deficient osteoclasts exhibit defective ruffled border formation and V-ATPase expression. Our findings suggest an important role of membrane binding of SWAP-70 for the regulation of actin dynamics, which is essential for podosome patterning, and thus for the resorptive activity of osteoclasts.
- Bone Rep. 2016 Jul 19;5:214-221
- 2016
- Medical Biology
- 28580389
- PubMed
Enabled by:
